DGH is broadly bestowed with the responsibility of managing the various activities with regard to Indian E&P acreages. They are in terms of awarding exploration blocks, executing production sharing contracts, monitoring developed fields etc.
India has an estimated sedimentary area of 3.14 million square kilometers, comprising 26 sedimentary basins.
Conventional E&P Acreages:
Petroleum Exploration Licenses (PEL) for conventional domestic exploration & production of crude Oil and natural gas were granted under four different regimes over a period time.
1. Nomination Basis:
Till the end of 1970s, Indian E&P industry was dominated by the two National Oil Companies (NOCs) - ONGC and Oil to whom PELs were granted on nomination basis. Exploration was primarily confined to onland and shallow offshore.
2. Pre-NELP Exploration Blocks:
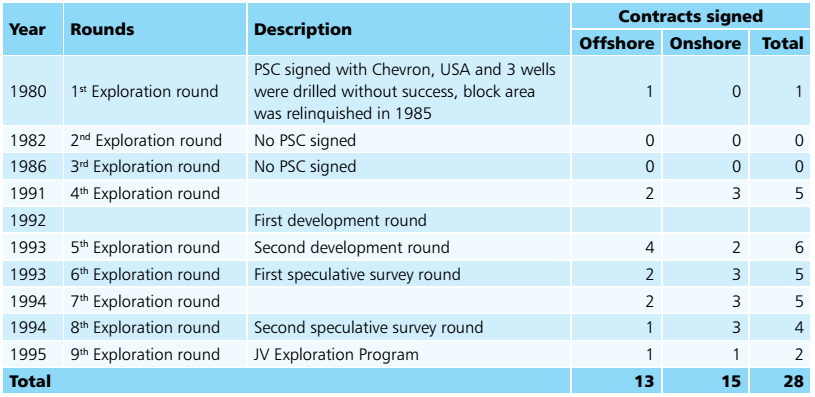
28 Exploration blocks were awarded to private companies between 1980 and prior to implementation of NELP where ONGC and Oil have the rights for participation in the blocks after hydrocarbon discoveries. In 1993, GoI offered blocks for geophysical and other surveys to update the information on hydrocarbon potential of India’s unexplored sedimentary basins. Once the surveys on these blocks were completed, they were to be offered in subsequent rounds of exploration. The second speculative survey round was launched in 1994 and the third round in 1995. The third round was called as Joint Venture Speculative Survey Round (JVSSR) with a provision of risk participation/cost sharing by DGH up to 50 %.
3. Pre-NELP Discovered Field or Development Rounds:
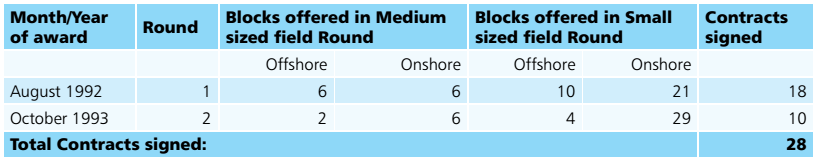
Government offered Petroleum Mining Lease (PML) of small/medium sized and discovered fields (proven reserves discovered by ONGC and Oil) to the private sector in August 1992 and October 1993. Production Sharing Contracts (PSCs) awarded during 1992-1993 had the distinctive feature of operators as private companies with ONGC/Oil as having Participating Interest. These rounds received overwhelming response from various private E&P operators. 28 contracts were signed by Government of India for 29 discovered fields. Under this regime, all statutory levies including royalty, cess, customs duties, were etc. payable by Contractor or Coventures. Signature/production Bonus was payable by companies to ONGC & Oil for small fields (1992) and for Medium and Discovered fields it was payable by Coventures
.
4. New Exploration Licensing Policy (NELP):
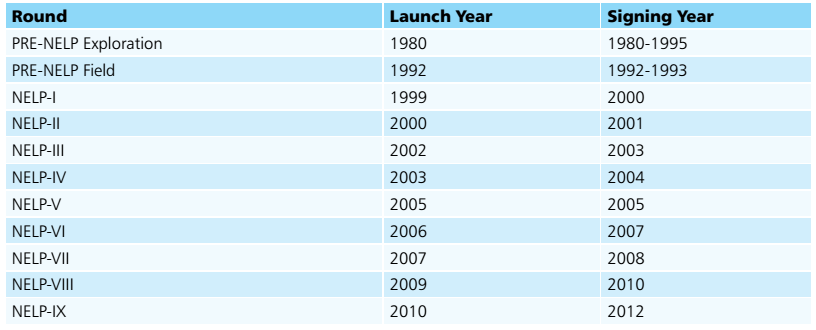
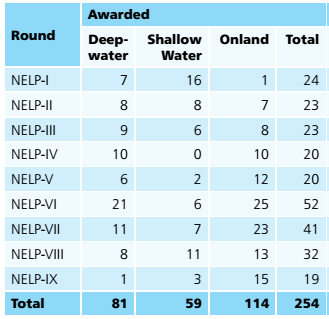
Under NELP, blocks were awarded to Indian, private and foreign companies through International Competitive Bidding process where NOCs viz. ONGC and Oil are also competing on equal footing. The Government has taken number of measures to bring in healthy competition and public participation by the way of NELP for exploration & production of Oil & gas in the country. NELP has not only accelerated the quest for hydrocarbon exploration, but has also brought the state of the art technology and efficiency of operations /management to the country.
CBM Acreages:
Coalbed Methane (CBM) is natural gas contained in coal. It consists primarily of methane, the gas we use for home heating, gas fired electrical generation and industrial fuel. CBM commonly is referred to as an “unconventional” form of natural gas because it is primarily stored through adsorption to the coal itself rather than in the pore space of the rock, like most “conventional” gas. The gas is released in response to a drop in pressure in the coal.
Coal Bed Methane (CBM), an unconventional source of natural gas is now considered as an alternative source for augmenting India’s energy resource. India has the fifth largest proven coal reserves in the world and thus holds significant prospects for exploration and exploitation of CBM. The prognosticated CBM resources in the country are about 92 TCF (2600 BCM) in 12 states of India. In order to harness CBM potential in the country, the Government of India formulated CBM policy in 1997 wherein CBM being Natural Gas is explored and exploited under the provisions of Oil Fields (Regulation & Development) Act 1948 (ORD Act 1948) and Petroleum & Natural Gas Rules 1959 (P&NG Rules 1959) administered by Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas (MOP&NG).
CBM blocks were carved out by DGH in close interaction with Ministry of Coal (MoC) & Central Mine Planning and Design Institute (CMPDI), Ranchi. Under the CBM policy, till date, four rounds of CBM bidding rounds have been implemented by MoP&NG, resulting in award of 33 CBM blocks [including 2 blocks on Nomination and 1 block through Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB) route] which covers 16,613 sq.km out of the total available coal bearing areas for CBM exploration of 26,000 sq.km. To date, most CBM exploration and production activities in India is pursued by domestic Indian companies. Total prognosticated CBM resource for awarded 33 CBM blocks, is about 62.4 TCF (1767 BCM), of which, so far, 9.9 TCF (280.34 BCM) has been established as Gas in Place (GIP).